Write data with third-party technologies
This page documents an earlier version of InfluxDB OSS. InfluxDB 3 Core is the latest stable version.
Configure third-party technologies to send line protocol directly to InfluxDB.
AWS Lambda via CloudFormation template
Write to InfluxDB with AWS Lambda, Amazon Web Services’ serverless offering. This example provides a CloudFormation template that collects earthquake from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) every hour and outputs it as line protocol into an InfluxDB bucket.
The template contains the following sections:
- Lines 1-20: Define variables that the template asks for when it’s installed.
- Lines 21-120: Handle a quirk of Lambda deployments that requires the Lambda assets to be in your region before deployment. As there is no elegant workaround, these 100 lines create an S3 bucket in your account in the region you’re creating the stack and copies in these resources.
- Lines 121-132: Define a role with basic permission to run the Lambda.
- Lines 133-144: Define a Python library layer. This layer packages the Python HTTP library, a Python S2 Geometry library, and the InfluxDB Python client library.
- Lines 145-165: Define the Lambda function, a short Python script zipped up in a file called
geo_lambda.zip. - Lines 166-188: Define an event rule with permission to run the Lambda every hour.
Deploy the template
- Log into your free AWS account and search for the CloudFormation service. Make sure you’re in the AWS region you want to deploy the Lambda to.
- Click Create Stack.
- In the Prerequisite - Prepare Template section, select Template is ready.
- In the Specify template section:
- Under Template source, select Amazon S3 URL.
- In the Amazon S3 URL field, enter the CloudFormation template URL:
https://influxdata-lambda.s3.amazonaws.com/GeoLambda.yml
- Click Next.
- Enter a name in the Stack name field.
- Enter the following InfluxDB details:
- Organization ID
- Bucket ID of the bucket the Lambda writes to
- Token with permission to write to the bucket
- InfluxDB URL
- Do not alter or add to any other fields. Click Next.
- Select the I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources check box.
- Click Create Stack.
After a few minutes, the stack deploys to your region. To view the new Lambda, select Services > AWS Lambda. On the Lambda functions page, you should see your new Lambda. The CopyZipsFunction is the helper copy function, and the GeoPythonLambda does the data collection and writing work:
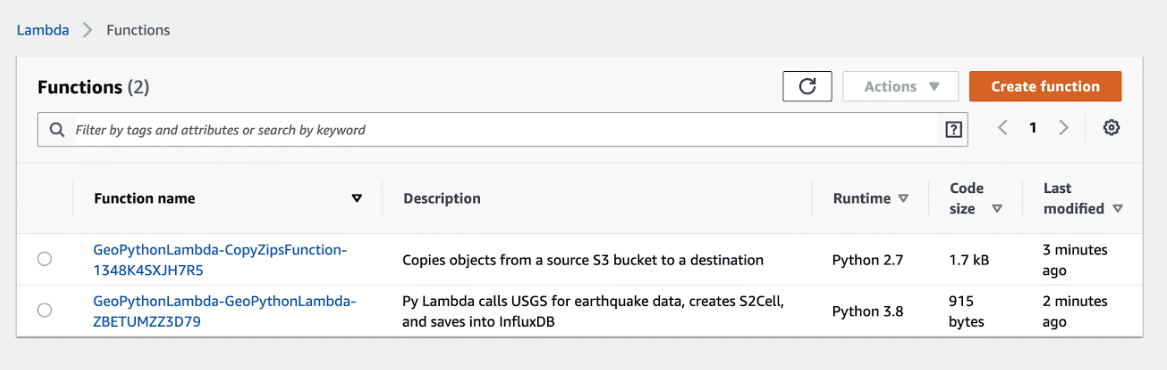
Verify your setup
GeoPythonLambda should run every hour based on the AWS Rule we set up, but you should test and confirm it works.
- Click
GeoPythonLambda, and then click Test. - The test requires an input definition, but this Lambda has no input requirements, so click through and save the default dataset.
- If the test is successful, a green Execution result: succeeded message appears.
With the data points written, when you log into your InfluxDB UI, you’ll be able to explore the geolocation earthquake data:
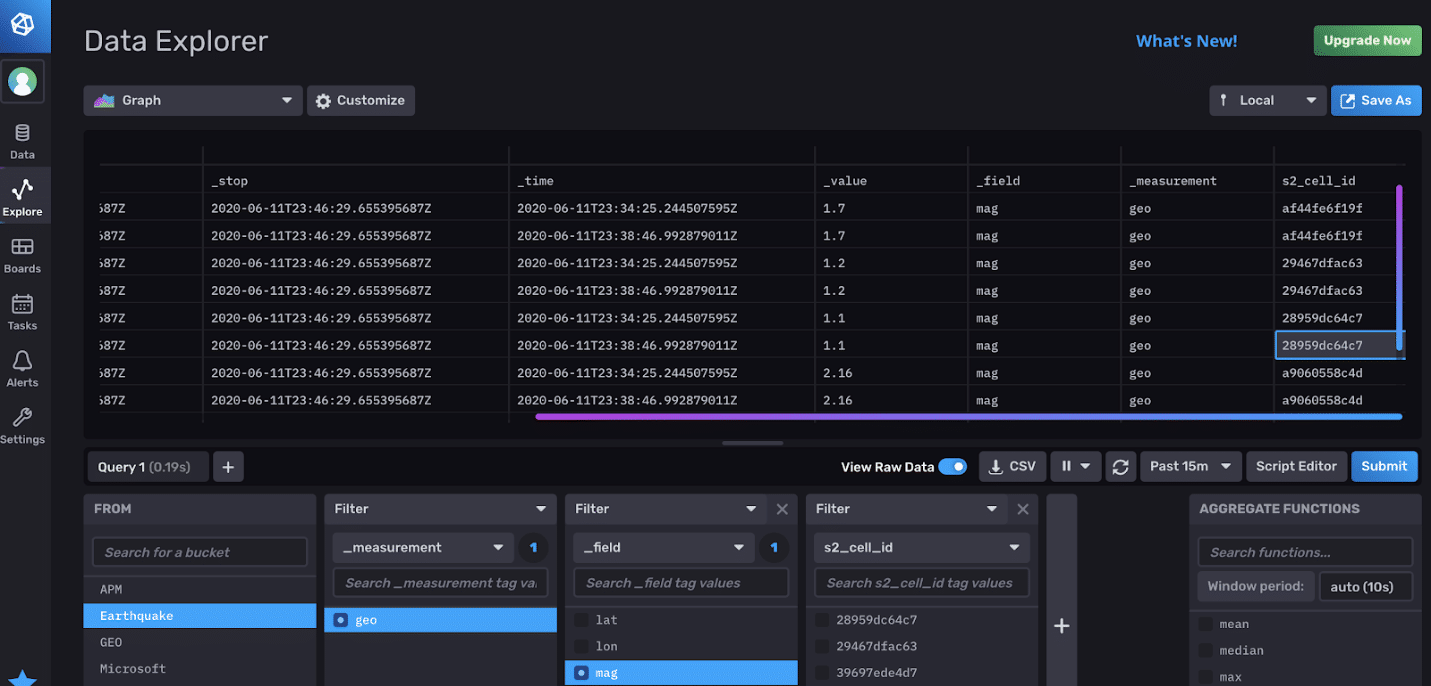
Was this page helpful?
Thank you for your feedback!
Support and feedback
Thank you for being part of our community! We welcome and encourage your feedback and bug reports for InfluxDB and this documentation. To find support, use the following resources:
Customers with an annual or support contract can contact InfluxData Support.
