List databases
Use the Admin UI, the influxctl database list command,
or the Management HTTP API to list databases in your InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated cluster.
Access the InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated Admin UI at console.influxdata.com. If you don’t have login credentials, contact InfluxData support.
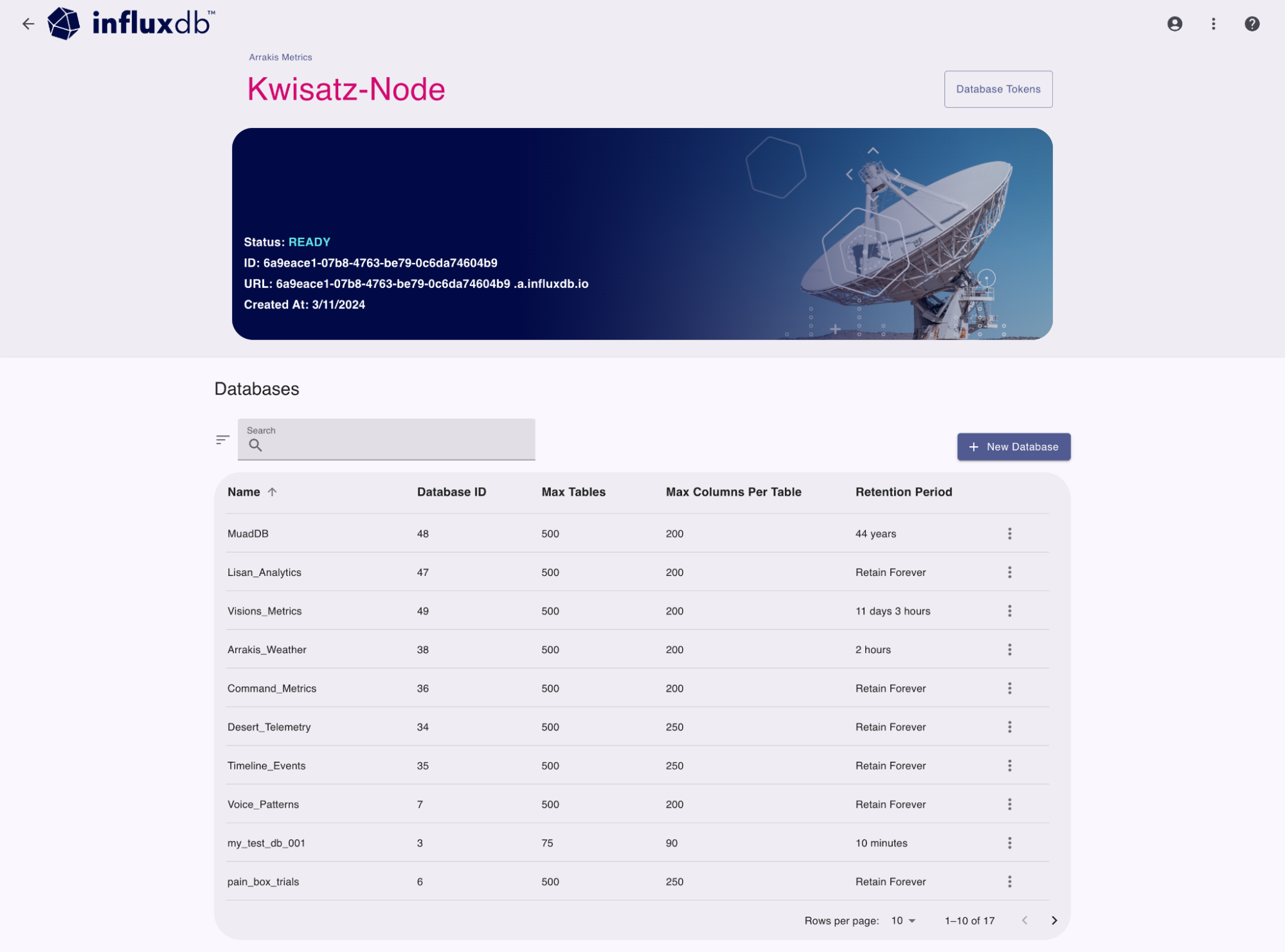
The database list displays the following database details:
- Name
- Database ID
- Max tables
- Max columns per table
- Retention period
You can Search for databases by name or ID to filter the list and use the sort button and column headers to sort the list.
Database management tools
The options button (3 vertical dots) to the right of any database provides additional tools:
- Copy Database ID: Copy the database ID to your clipboard
- Set Retention Period: Set the retention period for the database
- Delete Database: Delete the database
Manage database tables
To view database details and manage database tables, click the database row in the list.
Use the influxctl database list command
to list databases in your InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated cluster.
If you haven’t already, download and install the
influxctlCLI, and then configure aninfluxctlconnection profile for your cluster.In your terminal, run the
influxctl database listcommand and provide the following:- Optional: Output format
influxctl database list --format tableThis example uses cURL to send a Management HTTP API request, but you can use any HTTP client.
If you haven’t already, follow the instructions to install cURL for your system.
In your terminal, use cURL to send a request to the following InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated endpoint:
GET https://console.influxdata.com/api/v0/accounts/ACCOUNT_ID/clusters/CLUSTER_ID/databases
In the URL, provide the following credentials:
ACCOUNT_ID: The ID of the account that the cluster belongs to (see how to list cluster details).CLUSTER_ID: The ID of the cluster that you want to manage (see how to list cluster details).
Provide the following request headers:
Accept: application/jsonto ensure the response body is JSON contentAuthorization: Bearerand a Management API token for your cluster (see how to create a management token for Management API requests).
The following example shows how to use the Management API to list databases in a cluster:
curl \
--location "https://console.influxdata.com/api/v0/accounts/ACCOUNT_ID/clusters/CLUSTER_ID/databases" \
--header "Accept: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer MANAGEMENT_TOKEN"Replace the following in your request:
ACCOUNT_ID: the ID of the InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated account to create the database forCLUSTER_ID: the ID of the InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated cluster to create the database forMANAGEMENT TOKEN: a management token for your InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated cluster
Output format
The influxctl database list command supports two output formats: table and json.
By default, the command outputs the list of databases formatted as a table.
For easier programmatic access to the command output, include --format json
with your command to format the output as JSON.
The Management API outputs JSON format in the response body.
Retention period syntax
In table format, a retention period is a time duration value made up of a numeric value
plus a duration unit–for example, 30d means 30 days.
An infinite retention period means data won’t expire.
In JSON format, a retention period value is an integer (<int32>) that represents the number of nanoseconds–for example, 2592000000000 means 30 days.
A zero (0) retention period means data won’t expire.
Example output
+---------------+------------------+------------+-----------------------+
| DATABASE NAME | RETENTION PERIOD | MAX TABLES | MAX COLUMNS PER TABLE |
+---------------+------------------+------------+-----------------------+
| mydb1 | infinite | 500 | 250 |
| mydb2 | infinite | 500 | 200 |
| mydb3 | 24h | 100 | 200 |
+---------------+------------------+------------+-----------------------+[
{
"account_id": "0x0x0x00-0Xx0-00x0-x0X0-00x00XX0Xx0X",
"cluster_id": "X0x0xxx0-0XXx-000x-00x0-0X000Xx00000",
"database_name": "mydb1",
"retention_period_ns": 0,
"max_tables": 500,
"max_columns_per_table": 250
},
{
"account_id": "0x0x0x00-0Xx0-00x0-x0X0-00x00XX0Xx0X",
"cluster_id": "X0x0xxx0-0XXx-000x-00x0-0X000Xx00000",
"database_name": "mydb2",
"retention_period_ns": 0,
"max_tables": 500,
"max_columns_per_table": 200
},
{
"account_id": "0x0x0x00-0Xx0-00x0-x0X0-00x00XX0Xx0X",
"cluster_id": "X0x0xxx0-0XXx-000x-00x0-0X000Xx00000",
"database_name": "mydb3",
"retention_period_ns": 86400000000000,
"max_tables": 100,
"max_columns_per_table": 200
},
]Was this page helpful?
Thank you for your feedback!
Support and feedback
Thank you for being part of our community! We welcome and encourage your feedback and bug reports for InfluxDB Cloud Dedicated and this documentation. To find support, use the following resources:
Customers with an annual or support contract can contact InfluxData Support.
